[Spring] API 예외 처리
Updated:
1. 개요
API 예외는 같은 예외라도 컨트롤러에 따라 다르게 응답을 내려줘야 될 수도 있는데, 스프링에서는 다양한 상황에서 유연하게 API 예외를 처리할 수 있다. 이번에는 스프링에서 API 예외를 처리하는 방법에 대해 알아보도록 하자.
2. 개발 환경
-
Java 11
-
Spring Boot 2.7.5
3. @ExceptionHandler
@ExceptionHandler Annotation에 해당 컨트롤러에서 처리하고자 하는 예외를 지정하면, 지정한 예외 혹은 자식 예외 발생 시, 해당 Annotation이 붙은 메서드가 호출된다. 부모 예외와 자식 예외를 처리하는 두 개의 @ExceptionHandler가 존재하는 경우, 자식 예외를 처리하는 @ExceptionHandler가 우선순위를 갖는다.
3-1. 사용 방법
1) 직접 예외 지정
- @ExceptionHandler에 지정한 예외 혹은 그 자식 예외 발생 시, 해당 메서드 호출
1
2
@ExceptionHandler(IllegalArgumentException.class)
public ErrorResult illegalExHandle(IllegalArgumentException e) {}
2) 예외 지정 생략
- @ExceptionHandler에 예외 지정을 하지 않은 경우, 메서드 파라미터에 해당하는 예외 혹은 그 자식 예외 발생 시, 해당 메서드 호출
1
2
@ExceptionHandler
public ErrorResult userExHandle(UserException e) {}
3) 다양한 예외 지정
- 하나의 @ExceptionHandler에 여러 예외를 지정할 수 있다.
1
2
@ExceptionHandler({Exception1.class, Exception2.class})
public ErrorResult ex(Exception e) {}
3-2. 예제 코드
[ErrorResult.java]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ErrorResult {
private String code;
private String message;
}
[ApiExceptionV2Controller.java]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class ApiExceptionV2Controller {
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
@ExceptionHandler(IllegalArgumentException.class)
public ErrorResult illegalExHandler(IllegalArgumentException e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandler] ex", e);
return new ErrorResult("BAD", e.getMessage());
}
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResult> userExHandler(UserException e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandler] ex", e);
ErrorResult errorResult = new ErrorResult("USER-EX", e.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity(errorResult, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
@ExceptionHandler
public ErrorResult exHandler(Exception e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandler] ex", e);
return new ErrorResult("EX", "내부 오류");
}
@GetMapping("/api2/members/{id}")
public MemberDto getMember(@PathVariable String id) {
if (id.equals("ex")) {
throw new RuntimeException("잘못된 사용자");
}
if (id.equals("bad")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("잘못된 입력 값");
}
if (id.equals("user-ex")) {
throw new UserException("사용자 오류");
}
return new MemberDto(id, "hello " + id);
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
static class MemberDto {
private String memberId;
private String name;
}
}
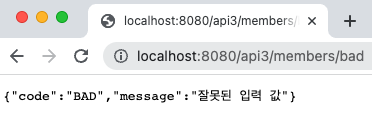
Line 5 ~ 10 : IllegalArgumentException 발생 시 해당 메서드를 호출하고, 400 응답
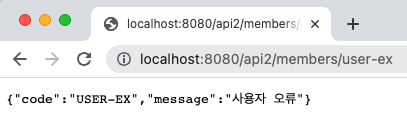
Line 12 ~ 17 : UserException 발생 시 해당 메서드를 호출
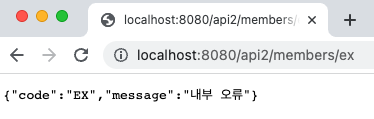
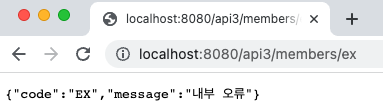
Line 19 ~ 24 : Exception 하위 예외 발생 시 해당 메서드를 호출하고, 500 응답
Line 28 ~ 30 : id가 ex인 경우 RuntimeException 발생
Line 31 ~ 33 : id가 bad인 경우 IllegalArgumentException 발생
Line 34 ~ 36 : id가 user-ex인 경우 UserException 발생
3-3. 실행 결과

4. @ControllerAdvice
@ExceptionHandler Annotation을 통해 API 예외를 처리할 수 있지만, 예외를 처리하는 코드와 정상 코드가 섞여있다는 단점이 있다. @ControllerAdvice Annotataion을 사용하면 두 코드를 분리시킬 수 있다. @RestControllerAdvice는 @ControllerAdvice와 동일하지만, @ResponseBody가 추가되어 있다.
4-1. 사용 방법
1) 대상 컨트롤러 지정
- 해당 컨트롤러에서 예외가 발생한 경우에만 적용된다.
1
2
@ControllerAdvice(annotation = RestController.class)
public class ExampleAdvice1 {}
2) 대상 패키지 지정
- 해당 패키지의 하위 컨트롤러에서 예외가 발생한 경우에만 적용된다.
1
2
@ControllerAdvice("org.example.controllers")
public class ExampleAdvice2 {}
3) 대상 클래스 지정
- 특정 클래스의 모든 컨트롤러에서 예외가 발생한 경우 적용된다.
1
2
@ControllerAdvice(assignableTypes = {ControllerInterface.class, AbstractController.class})
public class ExampleAdvice3 {}
4) 대상 미지정
- 모든 컨트롤러에서 예외가 발생한 경우 적용된다.
1
2
@ControllerAdvice
public class ExampleAdvice4 {}
4-2. 예제 코드
[ErrorResult.java]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ErrorResult {
private String code;
private String message;
}
[ExControllerAdvice.java]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice(basePackages = "hello.exception.api")
public class ExControllerAdvice {
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
@ExceptionHandler(IllegalArgumentException.class)
public ErrorResult illegalExHandler(IllegalArgumentException e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandler] ex", e);
return new ErrorResult("BAD", e.getMessage());
}
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResult> userExHandler(UserException e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandler] ex", e);
ErrorResult errorResult = new ErrorResult("USER-EX", e.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity(errorResult, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
@ExceptionHandler
public ErrorResult exHandler(Exception e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandler] ex", e);
return new ErrorResult("EX", "내부 오류");
}
}
Line 5 ~ 10 : IllegalArgumentException 발생 시 해당 메서드를 호출하고, 400 응답
Line 12 ~ 17 : UserException 발생 시 해당 메서드를 호출
Line 19 ~ 24 : Exception 하위 예외 발생 시 해당 메서드를 호출하고, 500 응답
[ApiExceptionV3Controller.java]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class ApiExceptionV3Controller {
@GetMapping("/api3/members/{id}")
public MemberDto getMember(@PathVariable String id) {
if (id.equals("ex")) {
throw new RuntimeException("잘못된 사용자");
}
if (id.equals("bad")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("잘못된 입력 값");
}
if (id.equals("user-ex")) {
throw new UserException("사용자 오류");
}
return new MemberDto(id, "hello " + id);
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
static class MemberDto {
private String memberId;
private String name;
}
}
Line 7 ~ 9 : id가 ex인 경우 RuntimeException 발생
Line 10 ~ 12 : id가 bad인 경우 IllegalArgumentException 발생
Line 13 ~ 15 : id가 user-ex인 경우 UserException 발생
4-3. 실행 결과

Leave a comment