[Spring] 빈 스코프(Bean Scope)
Updated:
1. 개요
빈 스코프는 빈이 존재할 수 있는 범위를 말한다. 이번에는 빈 스코프(Bean Scope)에 대해 알아보도록 하자.
- singleton : 하나의 빈만 생성해서 공유하는 스코프로, 스프링 컨테이너의 시작부터 종료까지 유지
- prototype : 요청 할 때마다 빈을 생성하는 스코프로, 스프링 컨테이너는 빈의 생성과 의존관계 주입까지만 관여
- web scope
- request : 요청이 들어오고 나갈 때 까지 유지되는 스코프
- session : 세션이 생성되고 종료될 때 까지 유지되는 스코프
- application : 서블릿 컨텍스트와 같은 범위로 유지되는 스코프
2. 싱글톤 스코프
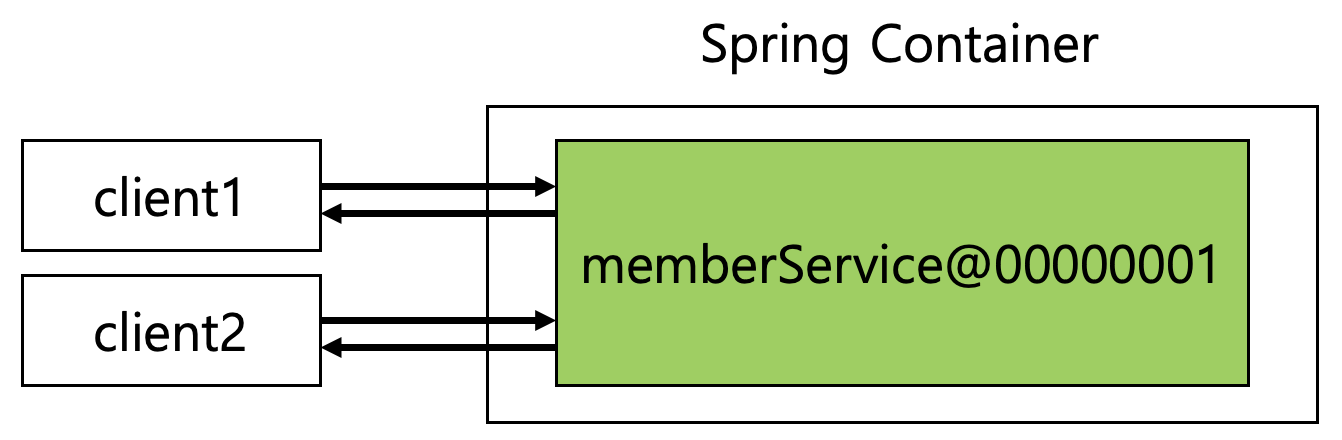
싱글톤 스코프를 사용하면, 스프링 컨테이너는 항상 같은 빈을 반환하고, 스프링 컨테이너 생성 시점에 초기화 메서드가 실행된다.
[SingletonTest.java]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
public class SingletonTest {
@Test
void singletonBeanFind() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SingletonBean.class);
SingletonBean singletonBean1 = ac.getBean(SingletonBean.class);
SingletonBean singletonBean2 = ac.getBean(SingletonBean.class);
System.out.println("singletonBean1 = " + singletonBean1);
System.out.println("singletonBean2 = " + singletonBean2);
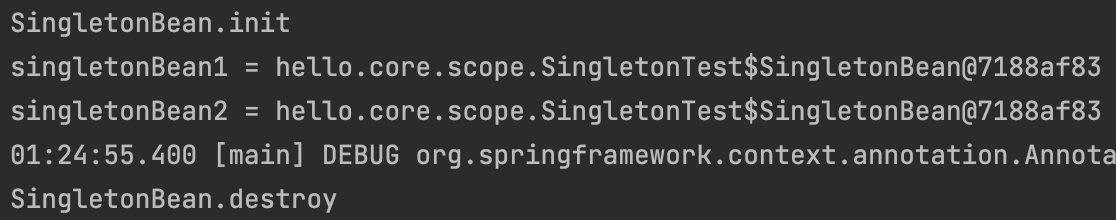
assertThat(singletonBean1).isSameAs(singletonBean2);
ac.close();
}
@Scope("singleton")
static class SingletonBean {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("SingletonBean.init");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("SingletonBean.destroy");
}
}
}
Line 17 : singleton 스코프 빈
[실행 결과]
3. 프로토타입 스코프
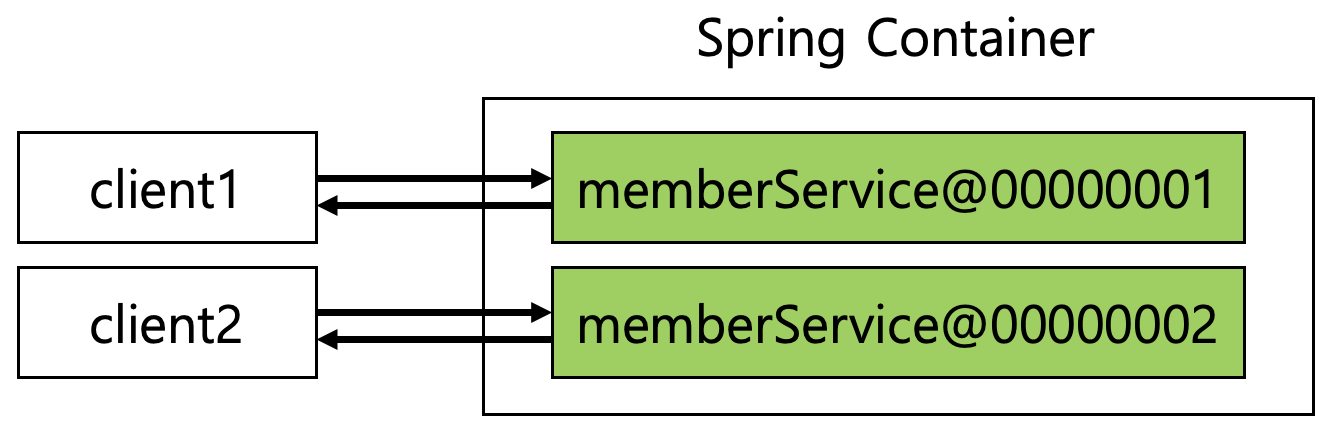
프로토타입 스코프를 사용하면, 스프링 컨테이너는 항상 새로운 빈을 생성해서 반환하는데, 스프링 컨테이너는 빈 생성, 의존관계 주입, 초기화 까지만 관여한다. 따라서 @PreDestroy와 같은 종료 메서드는 호출되지 않는다. 또한 스프링 컨테이너에서 빈을 조회할 때 생성되고, 초기화 메서드가 실행된다.
[PrototypeTest.java]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
public class PrototypeTest {
@Test
void prototypeBeanFind() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(PrototypeBean.class);
System.out.println("find prototypeBean1");
PrototypeBean prototypeBean1 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
System.out.println("find prototypeBean2");
PrototypeBean prototypeBean2 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
System.out.println("prototypeBean1 = " + prototypeBean1);
System.out.println("prototypeBean2 = " + prototypeBean2);
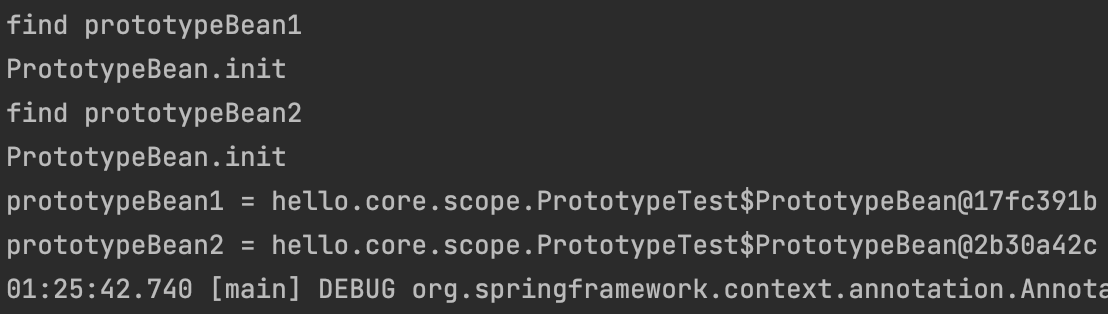
assertThat(prototypeBean1).isNotSameAs(prototypeBean2);
ac.close();
}
@Scope("prototype")
static class PrototypeBean {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("PrototypeBean.init");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("PrototypeBean.destroy");
}
}
}
Line 19 : prototype 스코프 빈
[실행 결과]
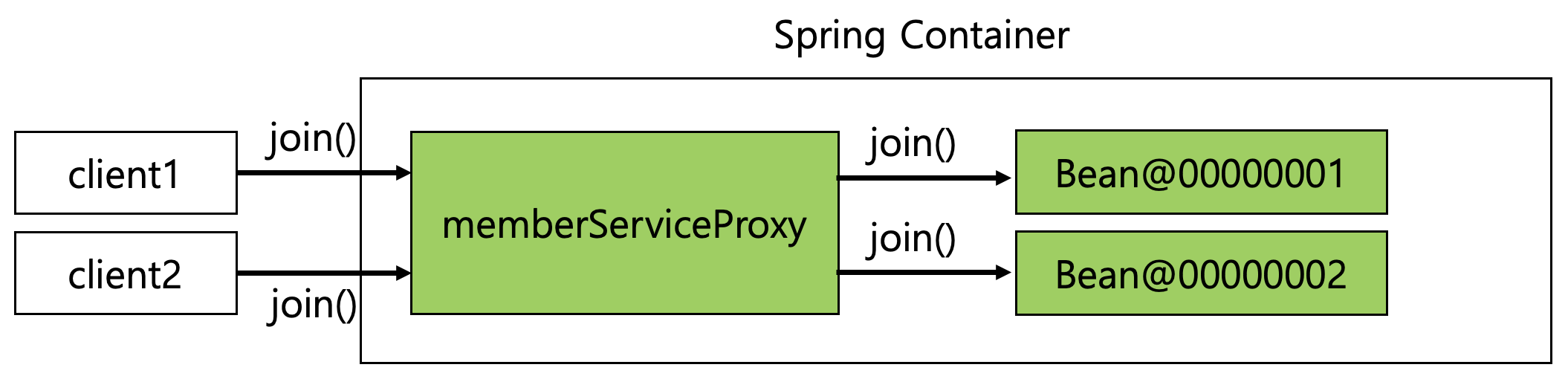
4. 웹 스코프
웹 스코프는 웹 환경에서만 동작하는 스코프로, 프로토타입 스코프와는 다르게 종료 시점까지 관리하므로 종료 메서드가 호출된다.
[MyLogger.class]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
@Component
@Scope(value = "request", proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS)
public class MyLogger {
private String uuid;
private String requestURL;
public void setRequestURL(String requestURL) {
this.requestURL = requestURL;
}
public void log(String message) {
System.out.println("[" + uuid + "]" + "[" + requestURL + "] " + message);
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
System.out.println("[" + uuid + "] request scope bean create: " + this);
}
@PreDestroy
public void close() {
System.out.println("[" + uuid + "] request scope bean close: " + this);
}
}
Line 2 : request 스코프 빈. request 스코프 빈은 실제 요청이 오는 순간 생성되므로, 프록시를 이용하여 스프링 애플리케이션이 실행되는 시점에는 가짜 객체가 생성되도록 설정
[LogDemoService.java]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class LogDemoService {
private final MyLogger myLogger;
public void logic(String id) {
myLogger.log("service id = " + id);
}
}
[LogDemoController.java]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
@Controller
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class LogDemoController {
private final LogDemoService logDemoService;
private final MyLogger myLogger;
@RequestMapping("/log-demo")
@ResponseBody
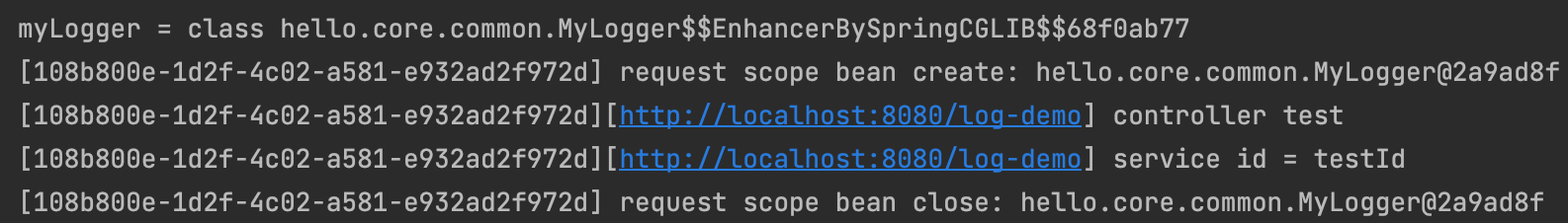
public String logDemo(HttpServletRequest request) {
String requestURL = request.getRequestURL().toString();
System.out.println("myLogger = " + myLogger.getClass());
myLogger.setRequestURL(requestURL);
myLogger.log("controller test");
logDemoService.logic("testId");
return "OK";
}
}
[실행 결과]

Leave a comment