[BOJ][2447] 별 찍기 - 10
Updated:
1. 문제 링크
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2447
2. 사용 알고리즘
분할정복
3. 풀이
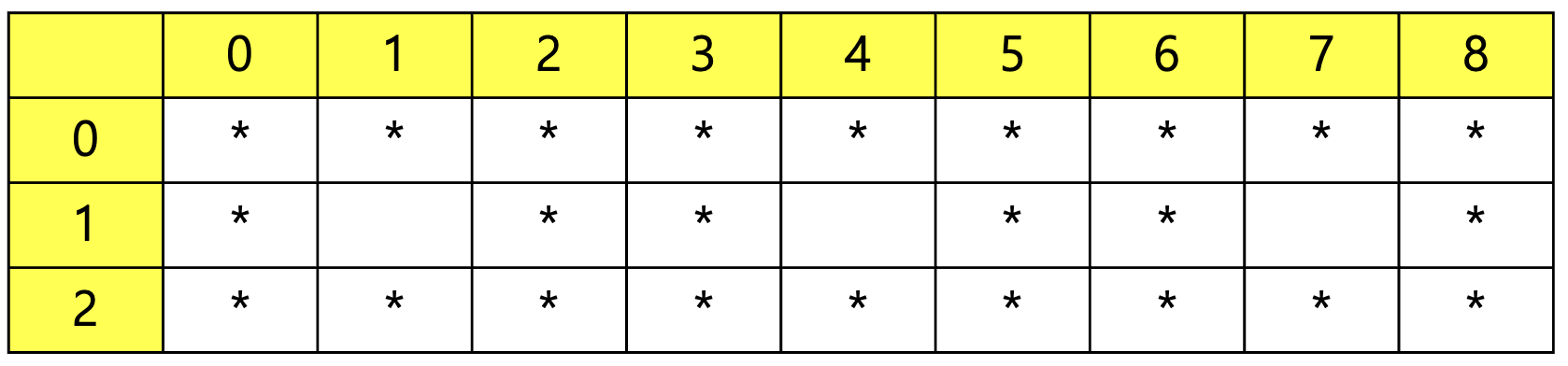
i와 j 모두 1, 4, 7 일 때 공백이므로 일반화하면, (i / 3) % 3 == 1 && (j / 3) % 3 == 1
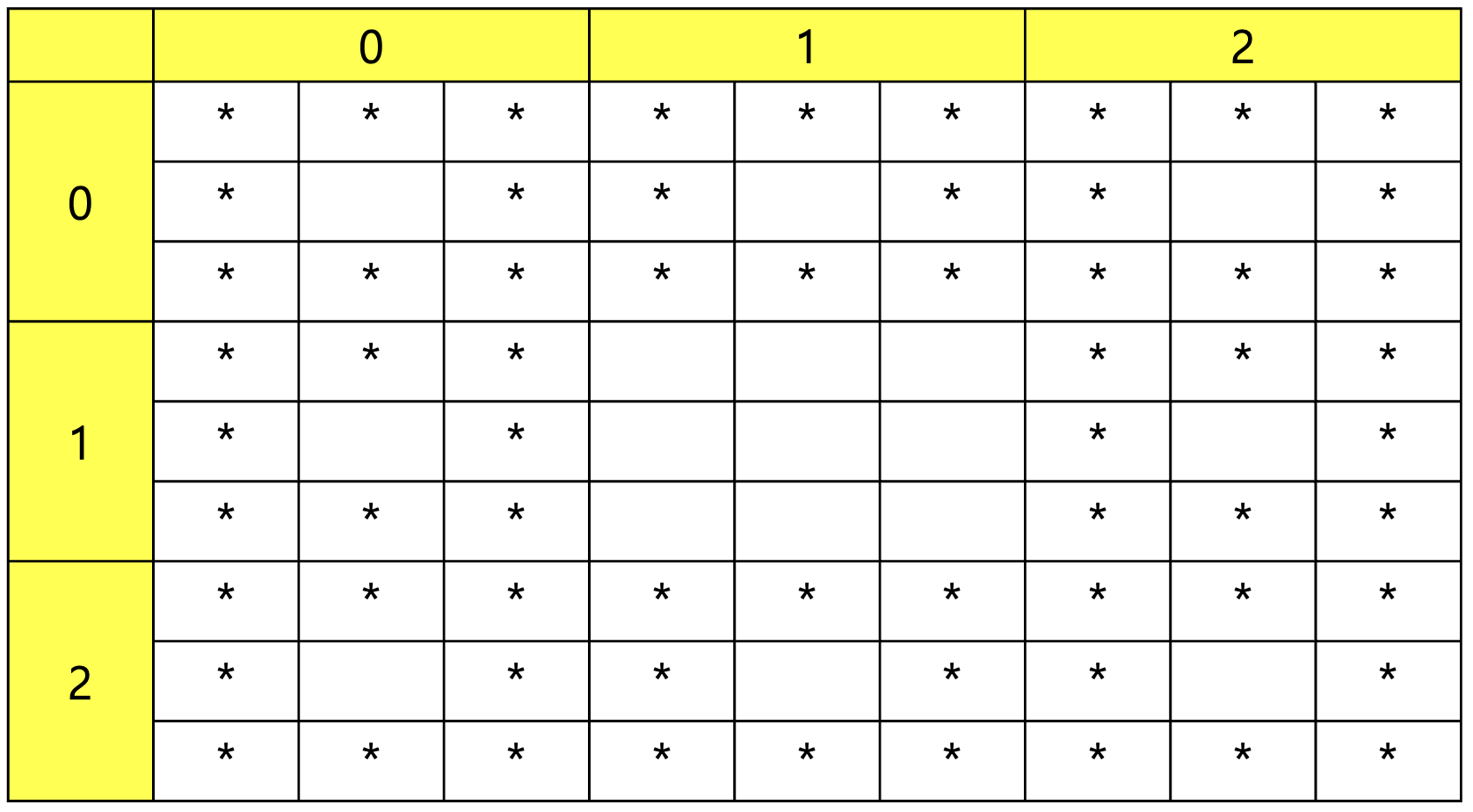
마찬가지로 (i / 3) % 3 == 1 && (j / 3) % 3 == 1을 통해 계산 가능
4. 소스 코드
4-1. C++
https://github.com/dev-aiden/problem-solving/blob/main/boj/2447.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void solve(int r, int c, int size) {
if(r / size % 3 == 1 && c / size % 3 == 1) cout << " ";
else if(size / 3 == 0) cout << "*";
else solve(r, c, size / 3);
}
int main(void) {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
int n; cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) solve(i, j, n);
cout << "\n";
}
cout << "\n";
return 0;
}
4-2. JAVA
https://github.com/dev-aiden/problem-solving/blob/main/boj/2447.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
private static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) solve(i, j, n);
sb.append("\n");
}
sb.append("\n");
System.out.println(sb);
}
public static void solve(int r, int c, int size) {
if(r / size % 3 == 1 && c / size % 3 == 1) sb.append(" ");
else if(size / 3 == 0) sb.append("*");
else solve(r, c, size / 3);
}
}

Leave a comment